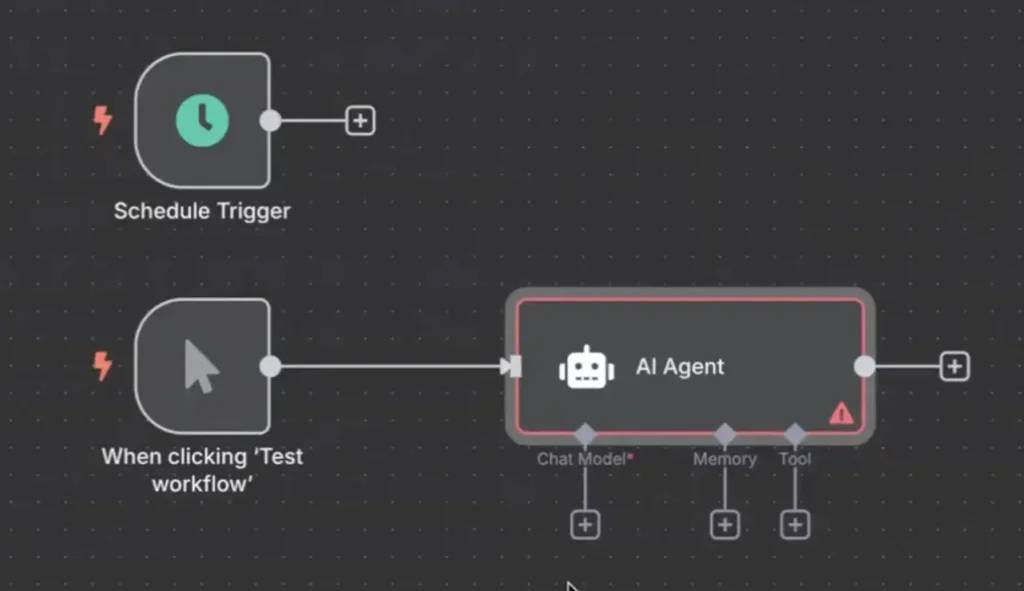
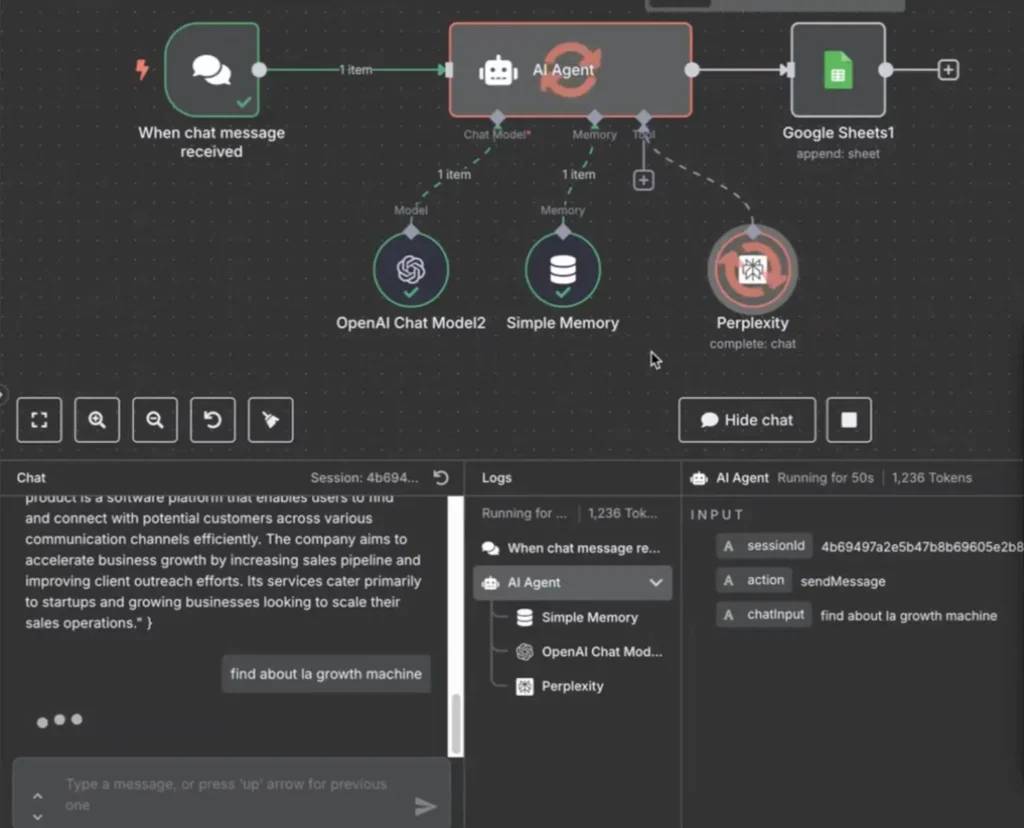
Features
What we do
Why people love us
Explore all our features
Get a demo
Join our
Live Product Tour
Playbooks
By need
Explore all playbooks
Resources
Learn with us
Free Resources
ACADEMY
HOT TOPICS
Academy
Wall of love
Pricing